Introduction
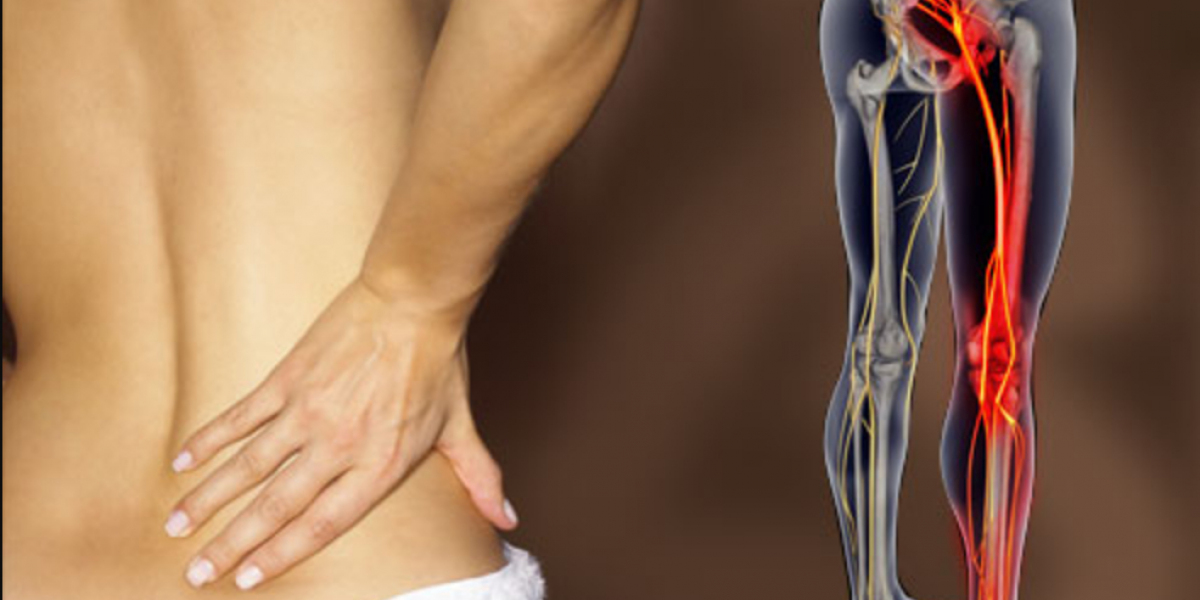
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on somatic pain. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of somatic pain, exploring its various types, underlying causes, and effective treatments. Somatic pain, also known as musculoskeletal pain, is a prevalent condition that affects millions of people worldwide. By understanding the nuances of somatic pain, individuals can better manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
Tapentadol 200mg is a larger dose of the medicine used to treat moderate to severe pain. Tapentadol 200mg, like the 100mg dosage, is an opioid analgesic. Its mode of action includes binding to the mu-opioid receptor and blocking norepinephrine reuptake, resulting in dual pain relief benefits.
What is Somatic Pain?
Somatic pain refers to pain that originates from the musculoskeletal system. Unlike visceral pain, which arises from internal organs, somatic pain is localized to the muscles, bones, joints, ligaments, and tendons. This type of pain is often described as sharp, throbbing, or aching and is typically well-localized to a specific area of the body.
Types of Somatic Pain
1. Superficial Somatic Pain
Superficial somatic pain originates from surface structures such as the skin and subcutaneous tissue. Common examples include cuts, burns, and abrasions. This type of pain is often sharp and localized.
2. Deep Somatic Pain
Deep somatic pain arises from deeper structures such as muscles, bones, and joints. Conditions like osteoarthritis, tendonitis, and fractures can lead to deep somatic pain. This type of pain is often described as dull and achy, with the intensity varying depending on the underlying condition.
Tapentadol 100mg is a medicine used to relieve moderate to severe pain. It is an opioid analgesic. The major method of action is to bind to the mu-opioid receptor and impede norepinephrine reuptake. This multimodal mechanism helps manage pain by influencing both the opioid and noradrenergic pathways.
Causes of Somatic Pain
Somatic pain can be triggered by a variety of factors, including:
1. Injury or Trauma
Injuries such as sprains, strains, fractures, and contusions can lead to acute somatic pain. These injuries often result from accidents, falls, or sports-related activities.
2. Inflammatory Conditions
Inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, bursitis, and tendonitis can cause chronic somatic pain. Inflammation within the musculoskeletal system can irritate nerves and lead to persistent discomfort.
3. Overuse or Repetitive Strain
Repetitive movements or overuse of certain muscles and joints can result in somatic pain. Conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome, tennis elbow, and rotator cuff injuries are common examples of overuse injuries that can cause persistent pain.
4. Structural Abnormalities
Structural abnormalities such as spinal misalignment, herniated discs, and joint degeneration can contribute to somatic pain. These abnormalities may place pressure on nerves or interfere with normal movement, leading to discomfort.
Buy tapentadol online is a centrally acting analgesic (pain reliever) that treats moderate to severe pain. It is classed as an opioid analgesic and comes in both immediate and extended-release forms. Tapentadol binds to mu-opioid receptors in the central nervous system and inhibits norepinephrine reuptake.
Treatments for Somatic Pain
Managing somatic pain often requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the underlying cause and the associated symptoms. Treatment options may include:
1. Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain associated with somatic conditions. In severe cases, prescription pain medications may be necessary to manage symptoms.
2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy techniques such as stretching, strengthening exercises, and manual therapy can help improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion. Physical therapists can tailor treatment plans to address specific musculoskeletal issues and reduce pain.
3. Injections
In some cases, steroid injections or joint injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief. These injections deliver medication directly to the affected area, targeting the source of discomfort.
4. Alternative Therapies
Complementary and alternative therapies such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, and massage therapy may offer relief for somatic pain. These modalities focus on restoring balance within the body and promoting natural healing processes.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and avoiding repetitive movements can help prevent exacerbation of somatic pain. Additionally, stress management techniques such as mindfulness meditation and deep breathing exercises can reduce tension and promote relaxation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, somatic pain is a complex condition that can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. By understanding the types, causes, and treatments of somatic pain, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their symptoms effectively. Whether through medications, physical therapy, injections, or alternative therapies, there are various options available for relieving somatic pain and restoring function. Remember, seeking professional medical advice is essential for developing a personalized treatment plan that addresses your unique needs.