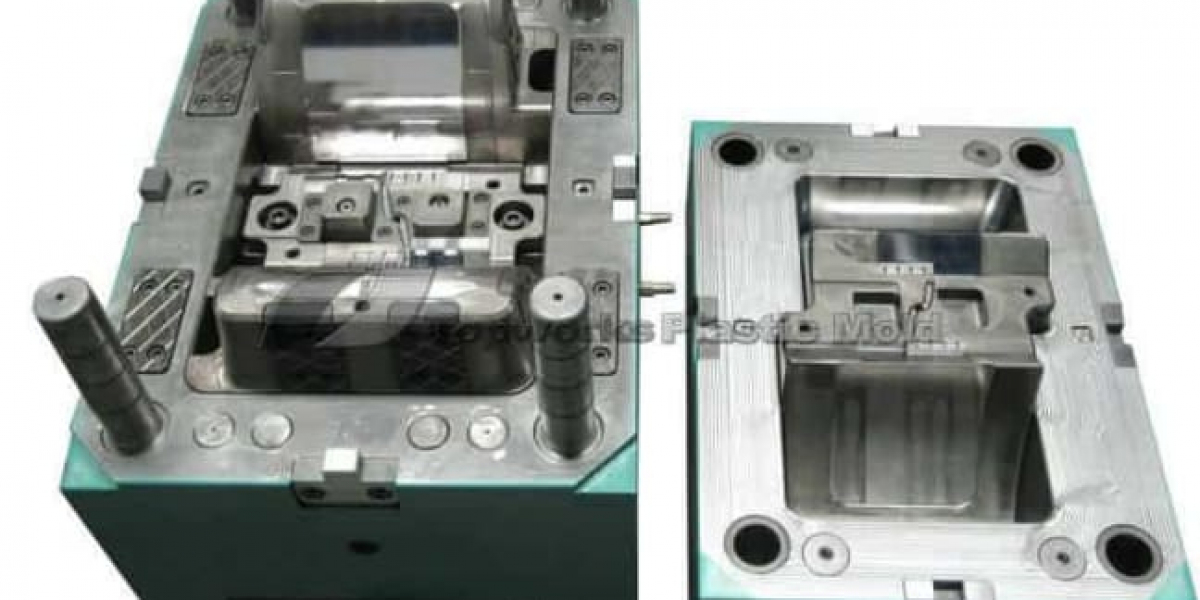
In the high-pressure world of injection molding, selecting the right material is crucial for a product's success. Two titans of the industry, polycarbonate and ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), often leave manufacturers scratching their heads. Both offer distinct advantages, and the optimal choice hinges on your specific project requirements.
This comprehensive guide dives deep into the fascinating world of polycarbonate injection molding and ABS injection molding . We'll explore their properties, applications, and guiding factors to help you pick the champion for your next project.
Unveiling the Powerhouse: Polycarbonate Injection Molding
Polycarbonate, a champion of strength and clarity, reigns supreme in applications demanding durability and optical excellence. This versatile material boasts exceptional impact resistance, making it ideal for high-traffic areas or products prone to accidental drops. Polycarbonate injection molding thrives in crafting bulletproof glass, medical devices, and safety equipment. Furthermore, its inherent flame retardancy adds another layer of safety.
Key Properties of Polycarbonate:
- Unequaled Impact Strength: Withstands significant blows without compromising integrity.
- Exceptional Clarity: Offers near-flawless transparency, perfect for lenses and displays.
- High-Temperature Resistance: Maintains structural integrity in hot environments.
- Flame Retardant: Provides an extra layer of safety in fire-prone situations.
- UV Resistant: Retains its properties even under prolonged exposure to sunlight (although some grades may require additives for enhanced UV protection).
Applications of Polycarbonate Injection Molding:
- Safety Equipment: Helmets, visors, and bulletproof glass.
- Medical Devices: Surgical instruments, housings for medical equipment.
- Electronics: Transparent housings for electronics and displays.
- Automotive Parts: Headlights, taillights, and instrument panels.
- Consumer Goods: Eyeglasses, sunglass lenses, and water bottles.
The all-rounder: ABS injection molding
ABS, a versatile and cost-effective workhorse, shines in applications where balance is key. It offers a good balance of strength, impact resistance, and chemical resistance, making it a popular choice for a wide range of products. Additionally, ABS readily accepts colorants and exhibits a pleasing surface finish, ideal for aesthetically driven projects.
Key Properties of ABS:
- Good Balance of Properties: Offers a blend of strength, impact resistance, and chemical resistance.
- Cost-Effective: An economical option compared to some high-performance materials.
- Excellent Processability: Flows easily in injection molding machines, reducing production complexity.
- Versatility in Color and Finish: Accepts a wide range of colors and finishes, enhancing aesthetics.
Applications of ABS Injection Molding:
- Consumer Electronics: Keyboards, cases for electronic devices, and appliance housings.
- Automotive Parts: Interior trim panels, dashboards, and wheel covers.
- Sporting Goods: Helmets, protective gear, and sporting equipment components.
- Building and Construction: Pipes, fittings, and electrical components.
- Toys: Durable and colorful toys for children.
The Decisive Factors: Choosing Between Polycarbonate and ABS Injection Molding
While both materials excel in their own right, selecting the champion requires careful consideration of your project's specific needs. Here are some key factors to guide your decision:
- Required Strength and Impact Resistance: If your product demands exceptional toughness, polycarbonate injection molding is the clear winner.
- Clarity and Transparency: When optical excellence is paramount, polycarbonate injection molding reigns supreme.
- Heat Resistance: For applications enduring high temperatures, polycarbonate injection molding offers superior performance.
- Cost Considerations: If budget is a primary concern, ABS injection molding often presents a more economical option.
- Chemical Resistance: ABS exhibits good resistance to a range of chemicals, making it suitable for specific applications.
- UV Resistance: Standard polycarbonate offers moderate UV resistance, while ABS is generally not UV resistant. However, additives can enhance UV resistance in both materials.
- Surface Finish and Aesthetics: If aesthetics are crucial, ABS offers a wider range of color and finish options.